The news: NASA has picked four teams to develop proposals for new missions. Each will receive $3 million to study their plans over the next nine months; then NASA will choose one or two of them to turn into full missions next year, based on their feasibility and scientific value. All of them are aimed at deepening what we know about the solar system, addressing pressing questions in planetary science.
The four potential missions:
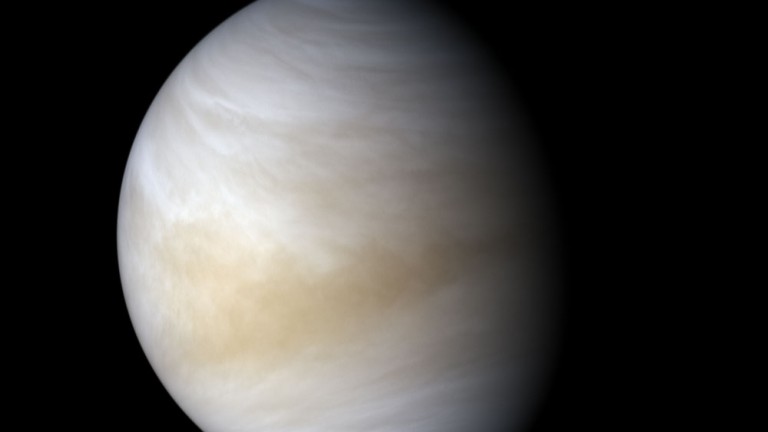
+ DAVINCI+ (Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging Plus) proposes sending a spacecraft down through Venus’s dense, hot atmosphere to measure its composition. This would help us to get a better picture of how the planet formed, and whether it ever had an ocean.
+ Venus Emissivity, Radio Science, InSAR, Topography, and Spectroscopy (VERITAS) would send powerful radar instruments to orbit Venus, mapping its surface to provide insights into its geologic history. The idea is that this would help us to better understand the planet’s surface and why it developed so differently from Earth.
+ Io Volcano Observer (IVO) proposes sending a spacecraft to make several close passes by Jupiter’s moon Io. It’s the most volcanically active body in the solar system, but little is known about its specific characteristics. The goal would be to work out how magma is generated on Io and exactly how its many massive volcanoes erupt, in the hope this helps our understanding of the formation and evolution of rocky terrestrial bodies.
+ Trident would send a spacecraft to fly past Neptune and its huge, icy moon Triton, to try to work out why it is so active despite its distance from the sun. It would map the moon and its active processes, and investigate whether it hosts a subsurface ocean, as predicted by the Voyager 2 mission that flew past Triton in 1989. This could help us to understand how habitable worlds form.
Current projects: All four of the missions are part of NASA’s Discovery program, which is responsible for projects like the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter and the Mars InSight Probe.